Tessamet: Histamine Detox
$89.00
6 in stock
Product Video:
Description:

Immune system Confusion
- Primitive humans had a lot of helminths (worms) to contend with.
- Too large to be attacked by the immune system, the body had to remove them mechanically.
- Mast cells release histamine which causes itching to make us scratch them off, coughing to get them dislodged from our respiratory tracts, a runny nose and sneezing to get them out of our sinuses and diarrhea to get them out of our intestines.
- With allergies, the body mistakes harmless allergens for parasites and tries to remove them.
- This response causes us symptoms.
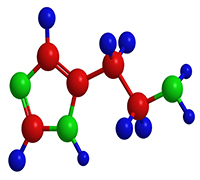
Histamine
- Histamine is both a hormone and a neurotransmitter and it has receptors all throughout the body.
- There are 4 classes of histamine receptors, named H1, H2, H3, H4.H1 and 2 go to the skin, gut and lungs and give us our classic allergy symptoms.
- Itchy or painful skin, food allergies, asthma and sinus inflammation.
- Less well known are that they also go to the heart and the reproductive organs.
- This means we can have an allergy heart, an allergic prostate, an allergic uterus. To properly deal with histamine 4 actions must be undertaken.
- 1- Re-educate the T cells of the immune system not to react to harmless allergens.
- 2- Suppress the over creation of histamine from the dietary amino acid histidine.
- 3- Stabilize mast and other cells that release histamine.
- 4- Increase serum DAO (diamine oxidase), the enzyme responsible for the break down of histamine.
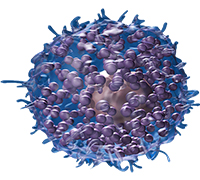
Mast cells
- Mast cells are an ancient part of our immune system predating antibodies.
- For some people, mast cells over-react to normal environmental elements and cause problems.
- In addition to releasing histamine, they can also release prostaglandins, leukotriene, tumor necrosis factor, trypase and heparin.
- Stabilizing mast cells is important in maintaining health.
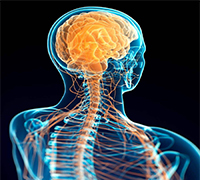
Brain allergy
- H3 receptors in the brain control the release of neurotransmitters.
- If body levels of histamine go too high, to protect the brain from toxic levels of histamine (and mania), H3 will LOWER histamine in the brain.
- This can lower the level of the neurotransmitters acetylcholine, dopamine, serotonin, norepinephrine and GABA. Low acetylcholine makes it hard to learn and remember.
- Low dopamine decreases motivation and in the extreme leads to Parkinson’s disease.
- Low serotonin leads to depression.
- Low Norepinephrine leads to difficulty focusing and ADHD.
- Low GABA makes it hard to relax or get deep sleep.
- Yes, a person can have an allergic brain and spinal column.
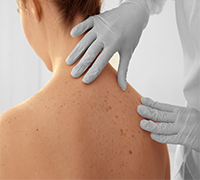
Skin
- Excessive histamine can activate H1 and H2 receptors in the skin causing rashes, itching and nerve pain.
- If the nerves of the sexual organs are affected, what should be experienced as pleasure can be uncomfortable instead.
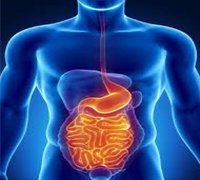
Gastrointestinal
- H1 and H2 receptors are found in the digestive tract.
- Excess histamine can lead to acid reflux, gas, stomach aches or loose stools.
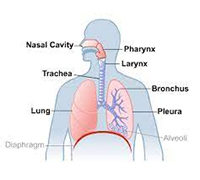
Lungs
- High levels of histamine can activate H1 and H2 receptors in the lungs and sinuses causing respiratory and sinus issues.
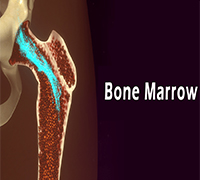
Immune cells
- High histamine can trigger H4 receptors in the bone marrow and immune system leading to dysfunctional immunity.
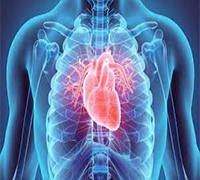
Cardiac
- High histamine can trigger H1 and H2 receptors in the heart leading to arrhythmias and high or low blood pressure. Yes, a person can have an allergic heart.
Ingredients:
- Rosmarinic acid
- EGCG
- quercetin
- DAO (diamine oxidase-porcine origin)
- sunflower lecithin
- MCT
- phosphatidyl choline
- ethanol
- glycerine
- plant cellulose
- candellia wax and purified water.
Protocols:
- Consider 1 capsule a day initially. Do not exceed 2 capsules per day.
- Do not continue if you experience an upset stomach or a rash lasting more than 3 days.
Tessamet: Histamine Detox
$89.00
6 in stock
Product Video:
Description:

Immune system Confusion
- Primitive humans had a lot of helminths (worms) to contend with.
- Too large to be attacked by the immune system, the body had to remove them mechanically.
- Mast cells release histamine which causes itching to make us scratch them off, coughing to get them dislodged from our respiratory tracts, a runny nose and sneezing to get them out of our sinuses and diarrhea to get them out of our intestines.
- With allergies, the body mistakes harmless allergens for parasites and tries to remove them.
- This response causes us symptoms.

Histamine
- Histamine is both a hormone and a neurotransmitter and it has receptors all throughout the body.
- There are 4 classes of histamine receptors, named H1, H2, H3, H4.H1 and 2 go to the skin, gut and lungs and give us our classic allergy symptoms.
- Itchy or painful skin, food allergies, asthma and sinus inflammation.
- Less well known are that they also go to the heart and the reproductive organs.
- This means we can have an allergy heart, an allergic prostate, an allergic uterus. To properly deal with histamine 4 actions must be undertaken.
- 1- Re-educate the T cells of the immune system not to react to harmless allergens.
- 2- Suppress the over creation of histamine from the dietary amino acid histidine.
- 3- Stabilize mast and other cells that release histamine.
- 4- Increase serum DAO (diamine oxidase), the enzyme responsible for the break down of histamine.

Mast cells
- Mast cells are an ancient part of our immune system predating antibodies.
- For some people, mast cells over-react to normal environmental elements and cause problems.
- In addition to releasing histamine, they can also release prostaglandins, leukotriene, tumor necrosis factor, trypase and heparin.
- Stabilizing mast cells is important in maintaining health.

Brain allergy
- H3 receptors in the brain control the release of neurotransmitters.
- If body levels of histamine go too high, to protect the brain from toxic levels of histamine (and mania), H3 will LOWER histamine in the brain.
- This can lower the level of the neurotransmitters acetylcholine, dopamine, serotonin, norepinephrine and GABA. Low acetylcholine makes it hard to learn and remember.
- Low dopamine decreases motivation and in the extreme leads to Parkinson’s disease.
- Low serotonin leads to depression.
- Low Norepinephrine leads to difficulty focusing and ADHD.
- Low GABA makes it hard to relax or get deep sleep.
- Yes, a person can have an allergic brain and spinal column.

Skin
- Excessive histamine can activate H1 and H2 receptors in the skin causing rashes, itching and nerve pain.
- If the nerves of the sexual organs are affected, what should be experienced as pleasure can be uncomfortable instead.

Gastrointestinal
- H1 and H2 receptors are found in the digestive tract.
- Excess histamine can lead to acid reflux, gas, stomach aches or loose stools.

Lungs
- High levels of histamine can activate H1 and H2 receptors in the lungs and sinuses causing respiratory and sinus issues.

Immune cells
- High histamine can trigger H4 receptors in the bone marrow and immune system leading to dysfunctional immunity.

Cardiac
- High histamine can trigger H1 and H2 receptors in the heart leading to arrhythmias and high or low blood pressure. Yes, a person can have an allergic heart.
Ingredients:
- Rosmarinic acid
- EGCG
- quercetin
- DAO (diamine oxidase-porcine origin)
- sunflower lecithin
- MCT
- phosphatidyl choline
- ethanol
- glycerine
- plant cellulose
- candellia wax and purified water.
Protocols:
- Consider 1 capsule a day initially. Do not exceed 2 capsules per day.
- Do not continue if you experience an upset stomach or a rash lasting more than 3 days.









